How does Consumer Electronics Housing provide a solid shield to protect devices?
Release Time : 2024-11-13
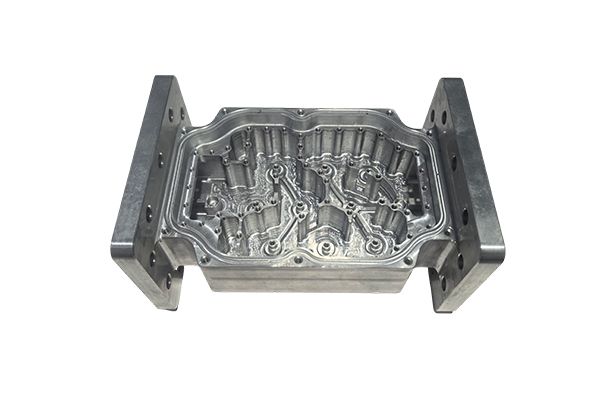
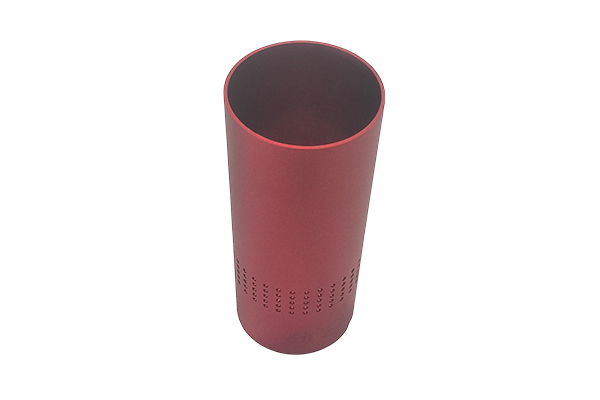
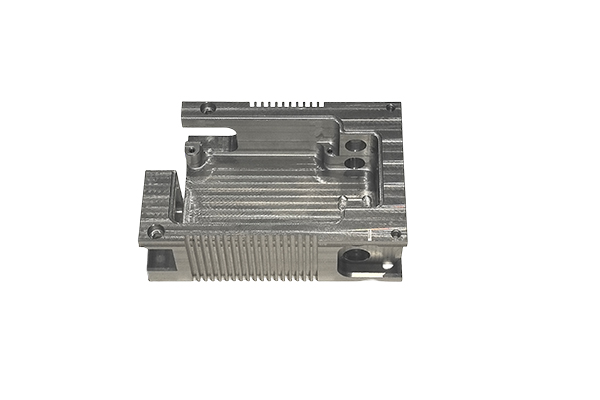
Consumer Electronics Housing plays a vital role in modern electronic devices. They are not only the appearance of the product, but also the key structure to protect the delicate electronic components and circuits inside.
1. Material selection
Consumer Electronics Housing usually uses a variety of materials to meet different functional requirements:
Plastics: light, easy to process, with good insulation properties, suitable for most consumer electronic products, such as mobile phones, tablets, etc.
Metals: such as aluminum and magnesium alloys, provide higher strength and durability, often used in high-end smartphones, laptops, etc.
Glass: beautiful, good optical performance, but relatively fragile, commonly seen on the back of mobile phones and some high-end devices.
Composite materials: combining the advantages of multiple materials, such as carbon fiber reinforced plastic, used in occasions that need to take into account both lightweight and high strength.
2. Design and function
The design of the housing needs to consider multiple factors:
Protection: prevent physical impact, splashing water and dust from entering, and protect internal components.
Heat dissipation: ensure that the heat generated during the operation of the electronic device can be effectively dissipated to prevent overheating.
Electromagnetic shielding: Prevent electromagnetic interference (EMI) from affecting device performance, especially in wireless communication devices.
Aesthetics: The appearance design must conform to market trends and user aesthetics to enhance product appeal.
3. Manufacturing process
Different housing materials and designs require different manufacturing processes:
Injection molding: Applicable to plastic housings, capable of efficiently producing parts with complex shapes.
CNC machining: Used for metal materials, providing high precision and surface finish.
Glass processing: Through chemical etching and mechanical polishing, a smooth and transparent surface is created.
Surface treatment: Such as anodizing, spraying, electroplating, etc., to enhance the aesthetics and durability of the housing.
4. Environmental impact
The selection of housing materials and the manufacturing process have a direct impact on the environment:
Sustainability: Choose recyclable materials and environmentally friendly processes to reduce the burden on the environment.
Life cycle: Design housings that are easy to disassemble and upgrade to extend the life of the device and reduce the generation of electronic waste.
Consumer Electronics Housing is not only a functional component, but also a key part of product design and user experience. Through careful material selection, design and manufacturing processes, the housing can effectively protect the device and enhance the market competitiveness of the product.
1. Material selection
Consumer Electronics Housing usually uses a variety of materials to meet different functional requirements:
Plastics: light, easy to process, with good insulation properties, suitable for most consumer electronic products, such as mobile phones, tablets, etc.
Metals: such as aluminum and magnesium alloys, provide higher strength and durability, often used in high-end smartphones, laptops, etc.
Glass: beautiful, good optical performance, but relatively fragile, commonly seen on the back of mobile phones and some high-end devices.
Composite materials: combining the advantages of multiple materials, such as carbon fiber reinforced plastic, used in occasions that need to take into account both lightweight and high strength.
2. Design and function
The design of the housing needs to consider multiple factors:
Protection: prevent physical impact, splashing water and dust from entering, and protect internal components.
Heat dissipation: ensure that the heat generated during the operation of the electronic device can be effectively dissipated to prevent overheating.
Electromagnetic shielding: Prevent electromagnetic interference (EMI) from affecting device performance, especially in wireless communication devices.
Aesthetics: The appearance design must conform to market trends and user aesthetics to enhance product appeal.
3. Manufacturing process
Different housing materials and designs require different manufacturing processes:
Injection molding: Applicable to plastic housings, capable of efficiently producing parts with complex shapes.
CNC machining: Used for metal materials, providing high precision and surface finish.
Glass processing: Through chemical etching and mechanical polishing, a smooth and transparent surface is created.
Surface treatment: Such as anodizing, spraying, electroplating, etc., to enhance the aesthetics and durability of the housing.
4. Environmental impact
The selection of housing materials and the manufacturing process have a direct impact on the environment:
Sustainability: Choose recyclable materials and environmentally friendly processes to reduce the burden on the environment.
Life cycle: Design housings that are easy to disassemble and upgrade to extend the life of the device and reduce the generation of electronic waste.
Consumer Electronics Housing is not only a functional component, but also a key part of product design and user experience. Through careful material selection, design and manufacturing processes, the housing can effectively protect the device and enhance the market competitiveness of the product.